|
I recently visited Monrovia, which in the words of P-Square, chopped my money. Food, accommodation, and transportation are much more expensive in Liberia than in any other West African country I have visited. It’s true that Liberia is a post-conflict country full of UN staff, who, when not struggling to help Liberia maintain its stability and get on its feet, are probably struggling to find enough things in Liberia to spend their money on. But Liberia also differs from other countries in West Africa in that the U.S. dollar is used in parallel to the Liberian dollar. Is it possible that dollarization could also contribute to higher prices? First, a couple of observations about money and prices in Liberia. The U.S. dollar and Liberian dollar are used interchangeably. There is no place that accepts only one. Generally, the U.S. dollars are used as large denomination bills, and the Liberian dollars are used in place of U.S. coins. (I didn’t see a single coin in Liberia.) Prices of imported goods in Liberian supermarkets are roughly the same as the dollar equivalent of prices of imported goods in Ghanaian supermarkets. Gas prices also seem to be similar, though a bit more expensive. It seems that the main difference in prices stems from differences in prices of services.
The fact that price differences are concentrated in services, or non-tradeables, makes me suspect that the high prices are in part due to dollarization, and here is why: in a non-dollarized economy, like Ghana, which uses the cedi, if the Ghanaian government pursues a loose monetary policy, the currency will depreciate relative to the U.S. dollar. This doesn’t affect the dollar price of imported goods—these are bought in dollars, so their price in Ghana cedis will just be inflated so that the equivalent price in dollars is unchanged. Other prices in the economy, however, are sticky. Employees have contracts with set wages, and people are used to paying a given price for hiring someone to sew a dress. As a result, the price of these non-tradeables stays constant in cedis, but becomes cheaper in dollar terms. (Note about monetary policy transmission in West Africa: In West Africa, business and consumer loans are much scarcer. So loosening monetary policy doesn’t lead to cheaper credit very quickly. It does, however, mean that cedi funds are more readily available to banks than U.S. dollar funds, which puts pressure on the exchange rate. So monetary policy transmission through exchange rates is more important in countries like Ghana, and happens more quickly, relative to transmission through interest rate mechanisms, compared to countries where large portions of the population have access to credit.) What this means is that Ghana, if has a trend of depreciating currency, can have low overall prices in dollar terms because, in dollar terms, prices for non-tradeables have fallen. Liberia, since it is dollarized, won’t see this effect. If Liberia prints more Liberian dollars, the exchange rate may change, with the value of the Liberian dollar declining, but prices in dollars will stay the same. This does, of course, attribute a level difference to an effect that applies to differences in rates of change, and my observations regarding prices of goods and services are anecdotal (Liberia doesn’t have good CPI data.) If you have comments on the plausibility of the theory, please comment!
5 Comments
Clearly, the nations of the world are not going to line up to let me randomize their monetary policy. But what if I could convince one to do so?
Randomized control trials (RCTs), when ethical and possible, present the most reliable way to measure the impact of policy. Units of randomization, for instance people, are put into a treatment group, who gets a program or policy, and a control group, that doesn't get the program or policy. You compare outcomes for the two groups to see the impact of the program. The key to the validity of the RCT is that the sample size has to be big enough that when you randomly divide into treatment and control, there are no important systemic differences between the two groups. Randomization isn't used to evaluate macroeconomic policies for 2 reasons: 1) it is usually too important for people to allow it to be randomized, and 2) it has to be enacted at a high level-- national or maybe state or province-- so it is difficult to get a large enough sample. But what if we randomized, not by entities like people or countries, but across years? For example, what if the Federal Reserve allowed me to randomly change the policy interest rate by +25 basis points, 0 basis points, or -25 basis points? Over a long enough time frame, the periods that fall into each randomization group should be statistically the same on average. This would allow us to look at the effect of the interest rate change on the economy. Of course, there are some kinks to be worked out. Similar to spillover effects, policy changes have impacts across multiple periods; however, these could be measured and accounted for. Another problem is checking the balance of the randomization. There would be no equivalent to a baseline, and you couldn't stratify, since you don't know the attributes of future time periods in advance. These problems would imply that you need a very large sample size. There are certainly other methodological challenges I haven't thought of. I imagine I will have plenty of time to think through them before the first problem-- the fact that politicians, who insist they can control things they can't, would never randomize something they can-- is solved. But if anyone hears about a central bank looking for a monetary policy consultant, let me know. The Ghana Cedi has depreciated noticeably in recent months. Similar depreciations were seen in 2000 and 2008, which, like 2012 were election years. (In 2004, also an election year, the cedi did not depreciate much.) 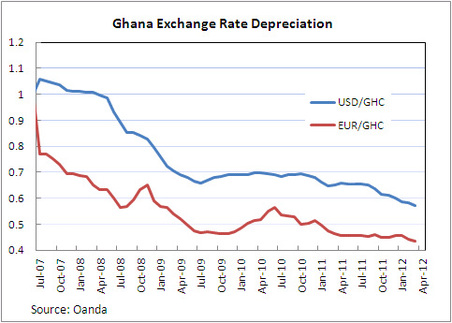 By the way, the actual currency code for the Ghana cedi is GHS. GHC refers to the old cedi. International finance nerds love currency codes. Does the Ghana cedi experience election year blues? If so, why? To address this question, I examine a few alternative explanations for the depreciation of the cedi: 1. The cedi depreciates in election years due to uncertainty about Ghana’s political and economic future. Uncertainty could result in cedi depreciation if it leads investors to pull their money out of Ghana, or to hesitate to invest in the first place. With the lead-up to the election looking more tumultuous than previous elections, and recent unrest in other West African countries, it would seem investors have reason to be cautious. It’s hard to find data to test this theory right now, as foreign investment data usually come at a lag. Foreign investment was strong in 2011 compared with 2010, but that says little about developments in the last half year or so. Uncertainty could also lead to depreciation if the cedi falls under speculative attack. The Bank of Ghana has attributed some of the depreciation to speculation that drives down the value of the cedi. (http://www.bog.gov.gh/privatecontent/MPC_Press_Releases/50th_MPC_Press_release-_Final_Copy.pdf) 2. The cedi depreciates in election years due to politically-motivated expansionary monetary policy by the Bank of Ghana. The incumbent party would benefit from a strong economy come election time. Short-term economic growth can be encouraged through expansionary monetary and fiscal policies. Increasing the money supply, however, eventually leads to inflation, which hinders the economy. The Bank of Ghana has actually raised policy interest rates in recent months, but you can’t necessarily look at policy interest rates alone to see if monetary policy is expansionary. Here’s why: the government of Ghana has been spending a lot of money (typical of an election year.) Normally, this would push up the government’s borrowing costs, and raise interest rates generally. However, if the central bank keeps rates constant rather than letting them rise, this has an expansionary effect. A better measure to look at is inflation. One-year inflation rates appear to be pretty steady, but these do not reflect very recent trends. The trouble with looking at monthly inflation is that prices in Ghana are highly seasonal, rising in the spring and then falling after harvest, and seasonally adjusted series are not released. Inflation in January and February was only somewhat higher than inflation in those same months over the last few years. While the key statistics that would be indicative of expansionary monetary policy are inconclusive at this point, the Bank of Ghana does acknowledge some other indicators of looseness. The Bank mentions that credit has eased, meaning money is easier to get, and that starting in 2011, there have been signs of liquidity overhang—meaning that banks have more cash than they want, causing interest rates to fall. The Bank mentions that these lower interest rates on cedi assets could be driving investments to other currencies with a higher rate of return. 3. The cedi depreciation is only coincidental to the election year, and is driven by other factors, including global economic conditions. There are some other factors that could be driving cedi depreciation. The first, mentioned by the Bank of Ghana, is that the depreciation is driven by demand for foreign currency to buy imports. Despite strong exports of oil, gold and cocoa, Ghana’s imports are growing faster than exports. A second possibility is that economic trouble in Europe is having a negative impact on the funds that are available to go to Ghana. This could account for a decline in investment in Ghana, if indeed such a decline is occurring. Remittances, however, appear to have remained robust, according to the Bank of Ghana. So what do I think? I think it is possible the election is having an effect, either on foreign investment, or on speculation in the currency market. I also think that the Bank of Ghana’s policies, politically motivated or otherwise, are responsible for it. While political turmoil is hard to address, a central bank can easily punish speculators and attract investors by raising interest rates. It appears that the Bank of Ghana is now taking steps to do just that, but earlier action might have nipped the depreciation and any speculation in the bud. My guess is that growing imports and a stagnant global economy may play roles, but not central ones. The West African CFA Franc, for example, has actually risen against the dollar since the beginning of the year. This suggests that at least some of the cedi’s downward trend is specific to Ghana’s. Luckily, that means that Ghana has the power to change it. Spotted this question on Yahoo! Answers (I was looking for examples of non-moral values but that's another story):
What is NOT a function of the Federal Reserve? A. Giving short-term loans to banks B. Controlling the money supply C. Regulating depository institutions D. Lending money to businesses for investment This is an intro to macro classic. If you said D, that was the correct answer. At least until the financial crisis. Some of the recently added facilities look like they could fall into that last category. For example, the Commercial Paper Funding Facility, which buys commercial paper directly from issuers. That sounds a lot like "lending money to businesses..." Time to add E. None of the Above The Reserve Bank of Australia became the first G20 central bank to raise interest rates today, increasing its policy interest rates by 25 basis points to 3.25%. Of course, Australia has done very well through the financial crisis, relatively speaking. It's banks have remained pretty strong, China has continued to demand Australia's commodity exports, and Australia has only had one quarter of negative GDP growth. (Australia's real GDP fell 2.8% at an annual rate in 2008Q4. while in the United States, recessions are declared by the NBER Business Cycle Dating Committee, many countries simply consider a recession to be in effect after two consecutive quarters of negative economic growth.)
The RBA's decision to raise interest rates resulted in a drop in the dollar. With Australia raising interest rates, investors know that there are assets out there where they can get higher returns, so low-yielding Treasuries don't look like such a good deal, despite their safety. The decision is also a vote of confidence in the world economy, which could increase investor's expected returns on assets other than Treasuries. As Australia and other countries (possibly Korea?) start raising interest rates ahead of countries like the United States and Japan, keep your eye out for a revitalization of the carry trade, where investors borrow in countries with low interest rates, and invest in countries with higher interest rates. One of the House Financial Services Republicans' financial regulation reform proposals is increased oversight of the Federal Reserve, including an explicit inflation target. Explicit inflation targets, where the central bank announces a specific inflation rate it intends to achieve, are used by a number of central banks around the world, including the European Central Bank and the Bank of England, both of which aim for 12 month consumer price inflation near 2%. In recent years, the European Central Bank has managed to keep inflation closer to 2% than the Federal Reserve. However, targeting alone doesn't tell the whole story. The European Central Bank is charged with considering price stability first, and economic growth second. The Federal Reserve is supposed to consider both equally. Thus, one would not necessarily expect the two monetary regimes to have identical inflation rates, even if they were both explicitly targeting 2% inflation.
An explicit inflation target can be useful to help build confidence in a central bank and ground inflation expectations-- if the central bank can meet the target. If it can't, the central bank risks losing confidence. Among central banks, the Federal Reserve may be least in need of building confidence, due to its long, respected record. If public confidence in the Federal Reserve were to falter, implementing an explicit inflation target might help. However, even though the Federal Reserve has become the target of some public blame for the financial crisis, markets appear to still have faith in its ability to maintain price stability. Inflation expectations (which can be gauged by looking at the difference between the yields on regular Treasury notes and the yields on notes indexed to inflation) have remained close to 2% for the medium to long term. This suggests that an explicit inflation target would do little to improve the functioning of the Federal Reserve. This is my first post, so let's get right to the substance. I just received an email asking me what I thought about this article: http://www.guardian.co.uk/commentisfree/2009/jan/20/george-monbiot-recession-currencies |
About Liz
I have worked in economic policy and research in Washington, D.C. and Ghana. My husband and I recently moved to Guyana, where I am working for the Ministry of Finance. I like riding motorcycle, outdoor sports, foreign currencies, capybaras, and having opinions. Archives
December 2016
Categories
All
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
